
Name: ____________________________________________________
Signature:__________________________________________________
Section:___________________________________________________
Answer all problems.
Do not start working until you are told to do so.
Following information may be useful:


formula sheets are also provided at the back of this test.
__________________________________________________________________________________
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. (25points)
Circle the right answers. Only one choice is correct. No penalty for wrong guess.
(note that there are several versions of the test. You may have different
choices for different versions.)
I. In which of the following cases the net force acting on the object is not zero:
A. A car moving at 55 miles per hour on a straight high way.
B. A person in an elevator ascending with constant velocity.
C. A space ship moving with constant velocity in outer space.
D. A shopping cart being pushed at constant velocity.
E. A free falling apple from the tree.
II. In Earth's gravitational field, which force is forming an action-reaction pair with the weight of the 10kg block?

A. Force exerted on the 2kg block due to the 1kg's weight.
B. Normal force from the 2kg block on the 1kg block.
C. Normal force from the table top.
D. Gravitational pull on Earth due to the 1kg block.
E. Weight of the 2kg block.
III. What is the frictional force if s and k are coefficient of static and kinetic friction respectively? The block is not moving.

A. 5N
B. 14.7N
C. 49N
D. 12.3N
E. None of above.
IV.

Which statement is not correct about the projectile:
A. At the highest point, the football travels instantaneously in horizontal direction.
B. The horizontal component of velocity is a constant for the whole projectile.
C. The horizontal component of the initial velocity can be calculated as 20cos35o in m/s.
D. For the same initial speed (20 m/s) the football will hit the same place if it is kicked at an angle of 55o from vertical, instead of 35o.
E The football is always accelerating towards the ground with an acceleration
of 9.8 m/s2.
V. In which of the following cases will the normal force from the table
top on the 2kg block equal to the 2kg weight?
A.

B.

C.

D.

E. In all cases the normal force from the table top equals to the weight of the 2kg block.
2. (25 points)

A person pushes a 20-kg lawn mower at constant speed with a force of 100N directed along the handle, which is at an angle of 35.0o to the horizontal along the handle (see figure). (a) Draw the free-body diagram showing all forces acting on the mower, Calculate (b) the horizontal retarding force on the mower, then (c) the normal force exerted vertically upward on the mower by the ground.
(a)



3. A basketball is shot right into the basket 6m away. The
basket is 7m above the basket (see figure). The horizontal component of
the initial velocity is given as 4m/s.
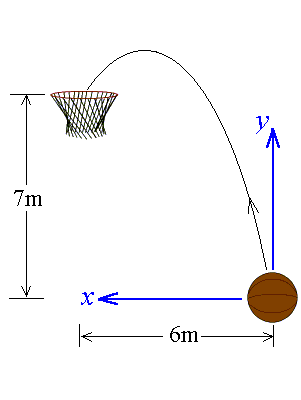
a. (5 points)
It takes how long for the basketball to reach the basket?

b. (12 points)
What is the vertical component of the initial velocity? What is the shooting angle?

c. (8 points)
What is the highest point of the projectile above the initial level of the basketball?


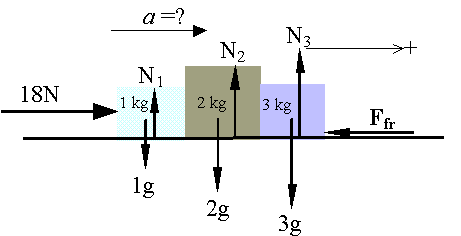
a. (5 points)
What is the acceleration of the blocks?


b. (7 points)
Calculate the normal force exerted by the 1kg block on the 2kg block.


c. (8 points)
Calculate the external force F.


d. (5 points)
If the three blocks are now placed on another horizontal surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.25. With the same applied force F, what will the acceleration?

Formula sheet
I. Physical constants:
g = 9.8 m/s2 (on Earth's surface) G= 6.67 10-11 Nm2/kg2
II. Kinematics equations





