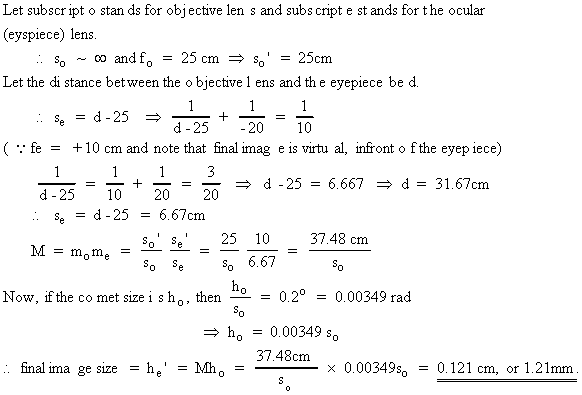
Time allowed: 1:00 p.m. to 1:50 p.m.
Answer all four questions (25 points for each question).
Write down and show your work clearly.
2.
a. (12 points)
A hyperopic (i.e. farsighted) person has to wear lenses of focal
length 33.33 cm to correct the vision. What is the near point
of that person?
Solution:

b. (13 points)
The same person is trying to read newspaper (without wearing correction
glasses) with a magnifying glass of focal length 5cm. If the newspaper
is placed 25cm in front of the eyes, what is the maximum distance
between the magnifying glass and the newspaper?
Solution:
3. Calculate 


a. (8 points)


Solution:

Superposition of coherent waves.
b. (7 points)


Solution:

Beating.
c. (7 points)


Solution:
4.

a. (10 points)
Fourier transform the voltage V(t) defined in the figure into
A(

Solution:
b. (10 points)
Consider a piece of electronic equipment with the following properties:
If a voltage of V0e-it is applied to the
input, then the output will be -iV0e-it
.
The voltage V(t) in part (a) is now connected to the input of
this equipment, what will be the output voltage as a function
of time? Sketch the output voltage.
Solution:
c. (5 points)
How would you like to call the equipment (choose one):
A. Frequency generator
B. Chopper
C. Integrator
D. Differentiator
E. Comparator
Give reasons:
D. Differentiator. As can be seen from the drawings in part (b),
V output is simply the derivative of V input. This is obviously
the case because the equipment is differentiating every harmonic
in the input.